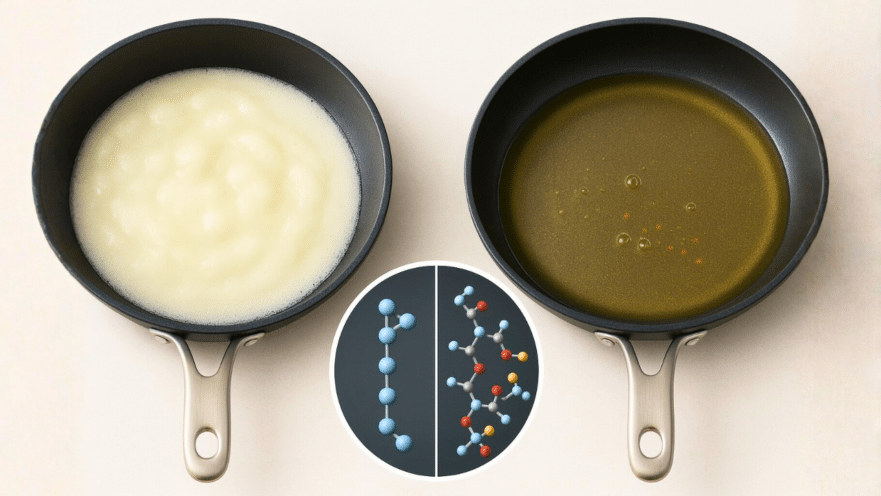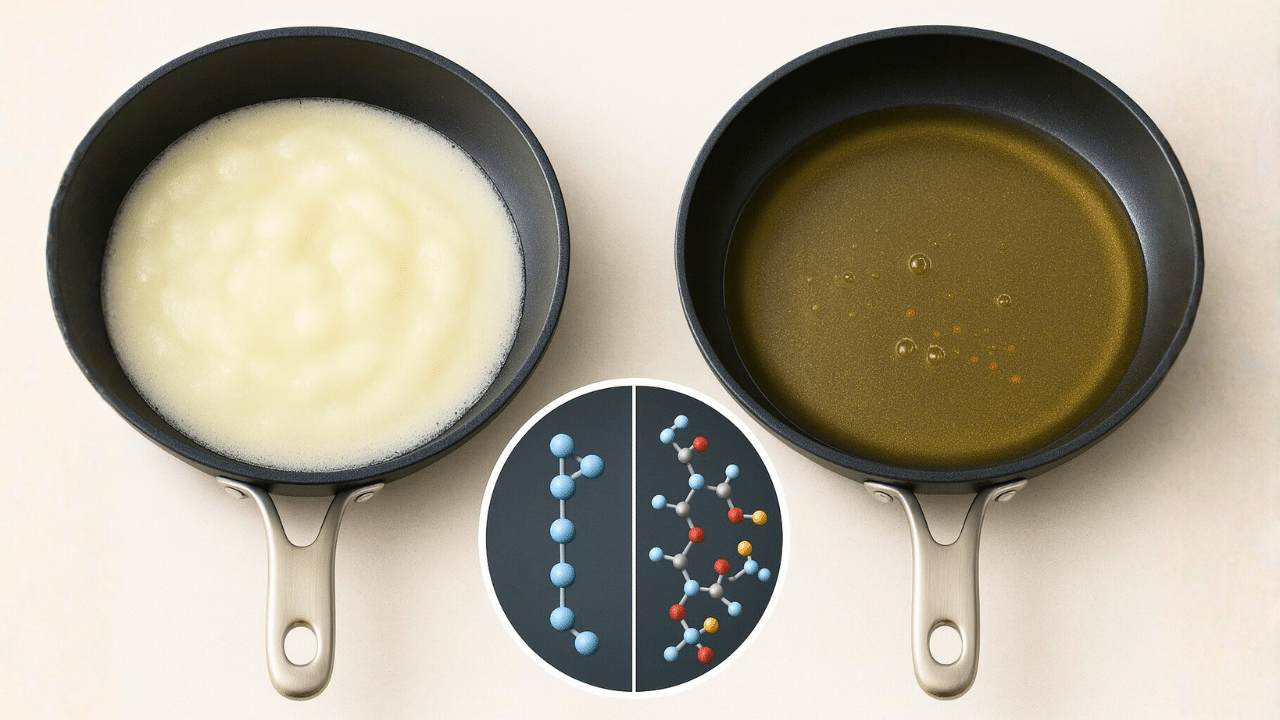
Have you ever wondered why our grandparents seemed to live healthier and longer, despite cooking with fats we’ve been told to avoid? Imagine walking into your grandmother’s kitchen on a Sunday morning—a whiff of comfort and real food fills the air as she scoops white lard into a sizzling pan. Decades ago, words like “heart attack” or “fatty liver” among kids were rare. So, what happened when vegetable oils took over our kitchens—and why has obesity tripled since?
Let’s unravel the truth the food industry doesn’t want you to know. In this article, you’ll learn the real science behind the fats you use everyday. We’ll uncover seven shocking facts about cooking oils so you’ll know exactly how to protect your family’s health. Ready? Let’s get started. (Based on the insights of Dr. Andre Wambier)
Key Takeaways
- Saturated animal fats like lard were replaced with vegetable oils due to incomplete, industry-funded science.
- Modern vegetable oils are chemically processed and may contain harmful compounds.
- Reused and heated vegetable oils create toxic substances linked to chronic diseases.
- Not everyone should consume lard freely—dietary context and metabolic health matter.
- Olive oil (extra virgin) is a safer and scientifically validated option for most people.
- The difference between food and poison often comes down to quantity and context.
- Science evolves: Your kitchen choices today can protect your family for generations.
1. The Demonization of Animal Fats Was Based on Flawed Science
Ever wonder how your grandmother lived a sharp, healthy life to 90 and beyond, cooking daily with lard? In the 1950s, a scientist named Ancel Keys published a now-famous chart linking saturated fat consumption to heart disease. But there’s a catch: he cherry-picked data from just six countries—even though data from 22 countries was available! When you include them all, the link between saturated fat and heart disease gets very fuzzy. Countries like France, who eat lots of saturated fat, actually have low rates of heart disease—a paradox conveniently left out because it didn’t fit the theory.
Fast forward, and the vegetable oil industry, along with sugar interests, funded research to blame saturated fats while hiding the risks of sugar. It’s not conspiracy; receipts and journal articles prove it. For decades, you were taught that your grandma’s lard was poison, and chemically refined soybean oil was heart-healthy. But is that the real story?
2. Vegetable Oils Are Chemically Processed—and Not as Natural as You Think
Think the golden oil in your bottle is just squeezed from a soybean or sunflower? Think again. The food industry uses chemical solvents like hexane (a petroleum-derived substance) to extract the oil. Then, it’s bleached and deodorized to look and smell appealing. Worse, these oils are stored for months in plastic bottles, where they can absorb microparticles and hormone-disrupting chemicals from the packaging. You could be ingesting more than just oil—think tiny plastics and chemicals that confuse your body’s natural hormones.
3. Reused and Heated Vegetable Oils Are Factories of Toxic Compounds
Most vegetable oils used for frying (soy, corn, sunflower, canola) are polyunsaturated and highly unstable. When heated—especially repeatedly—they break down and release toxic chemicals called aldehydes, especially one called 4-HNE (4-hydroxynonenal). Studies show heating vegetable oil to typical frying temperatures (185°C) produces these dangerous substances in just two hours, and the levels keep rising. These toxins migrate into your food (like French fries) and have been linked to Alzheimer’s, heart disease, liver problems, diabetes, and even cancer. Disturbingly, the amounts go up the older you get and the more often the oil is reused—so beware of that reused oil at restaurants!
4. Cooking Oils Can Be Hormone Disruptors
Remember: Oils love fat, and they also love absorbing chemicals from their containers, especially from cheap plastic (PET) bottles. Over time, vegetable oils can leach hormone-mimicking substances called phthalates and endocrine disruptors into your food. These stray chemicals can wreak havoc on your body’s hormone balance, especially if consumed regularly. In contrast, your grandma’s lard came in tin or glass containers, dodging these modern pitfalls.
5. Excess Omega-6 Oils Fuel Silent Inflammation
Tired joints, chronic fatigue, that heavy-body feeling—did you know excess omega-6 fats in vegetable oils might be to blame? Soybean oil is loaded with omega-6 fatty acids, which, when not balanced with omega-3s, create a pro-inflammatory state in your body. Chronic inflammation is the root of many modern diseases, including arthritis, heart disease, and even depression. Lard, by comparison, has a more neutral fatty acid profile for cooking.
6. Cholesterol Myths—The Real Story
Worried that animal fats will clog your arteries? Here’s the deal: What actually causes arterial blockages is not eating fat, but chronic inflammation and oxidation within your body. Blaming lard alone is like blaming the firefighter for the fire. That said, the science remains nuanced—a blanket recommendation for everyone to use lard would be irresponsible. If you already have high cardiovascular risk, or chronic conditions, consult your doctor. Some studies suggest lard can raise LDL (“bad”) cholesterol in certain populations, but for many, the real villain is the oxidized vegetable oil, sugar, and sedentary lifestyle.
7. Not Everyone Should Use Lard Freely: Who Needs to Be Careful?
Here’s the science-based, honest answer: Lard and saturated fats are more stable than vegetable oils—but overconsumption can pose risks, especially for those with diabetes, severe insulin resistance, or genetic cholesterol disorders. Research from Brazil shows too much lard in the diet can impair insulin action in the brain, disrupting appetite and blood sugar regulation. For people with these risks, extra virgin olive oil is the clear winner—it’s rich in antioxidants and polyphenols, tolerates heat well, and is heart-protective even when cooked.
But What About Olive Oil and Modern Choices?
Extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) is a safe, science-backed choice for nearly everyone, especially those worried about heart health or diabetes. Don’t buy into the myth that olive oil becomes toxic when heated—high-quality EVOO stands up to typical cooking temperatures thanks to its natural antioxidants. Avocado oil is another reliable, stable option. Science says: Avoid and gradually replace industrial, refined oils wherever possible.
The Take-Home Experiment You Can Try
Want proof for yourself? Try this simple kitchen test: heat a bit of soybean oil, lard, and extra virgin olive oil (in separate pans) to the same temperature. Smell each one. Lard stays stable and nearly scentless, olive oil is pleasant, but the soybean oil smells odd, acrid, or like plastic—that’s the toxins being released! Your nose can detect what science has proven.
Conclusion
It’s time to rethink what’s really healthy in your kitchen. The so-called healthy gold in bottles—refined vegetable oils—has been exposed by science as unstable, inflammatory, and potentially toxic when heated. Your grandma’s good old lard isn’t the villain it was made out to be, but moderation matters, especially if you have certain health risks. The best choice for most? Extra virgin olive oil or avocado oil. Real food, not chemistry sets—just like your ancestors knew.
Source: Dr. Andre Wambier