Levothyroxine is a synthetic thyroid hormone, widely used to treat hypothyroidism and other thyroid-related issues. It mimics the effects of naturally produced thyroid hormones. It’s one of the most prescribed medications globally, with millions relying on it daily. However, a significant portion of users are unaware of key aspects of how it works, leading to improper usage and reduced effectiveness. This can turn a helpful ally into a source of problems. This post aims to clarify what levothyroxine is, its uses, proper administration, precautions, and answers to frequently asked questions. (Based on the expertise of Dr. Alberto Sanagustín.)
What Is Levothyroxine and What Is It Used For?
Levothyroxine is a medication that acts as a synthetic version of T4, a hormone naturally produced by your thyroid gland. The thyroid gland is crucial for regulating metabolism, and when it underproduces thyroid hormone (a condition called hypothyroidism), it can lead to a range of symptoms. These often include fatigue, weight gain, dry skin, hair loss, and feeling constantly cold. Levothyroxine helps to replace the missing hormone, thereby restoring balance to your metabolism and other bodily functions.
It’s also used in certain cases following thyroid surgery to manage the growth of nodules within the thyroid. Generally, it’s a safe and effective treatment when taken correctly under medical supervision.
How Does Levothyroxine Work in Our Bodies?
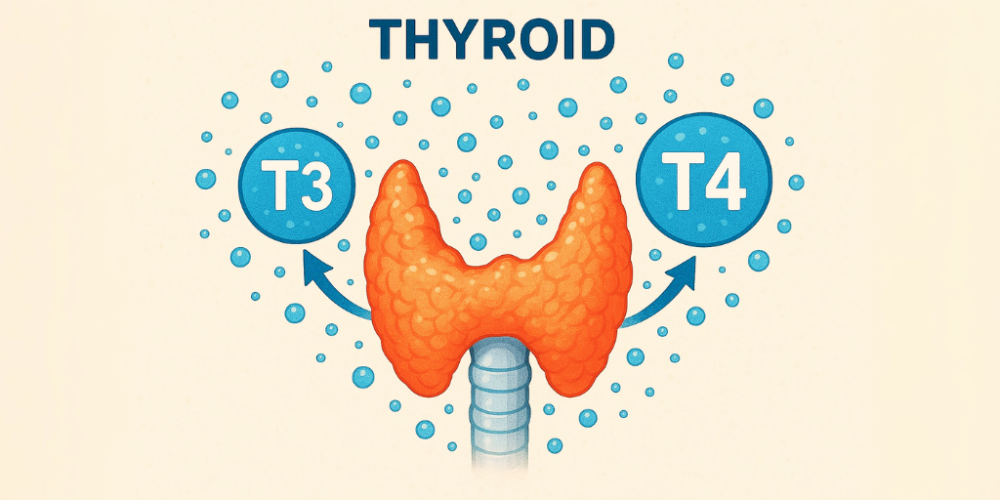
As mentioned, levothyroxine provides the T4 hormone. When you take it orally, your body absorbs it and converts it into T3, which is the active form of thyroid hormone. T3 influences numerous bodily functions, including metabolism (how quickly your body converts food into energy), body temperature, heart rate, brain function, and even the workings of your intestines.
For individuals with hypothyroidism, levothyroxine acts as a replacement for the hormones their thyroid isn’t producing sufficiently. This helps their body regain a state of balance. The dosage of levothyroxine often needs adjustment – it might be increased or decreased – to ensure it’s effectively performing its function. Too much or too little can cause significant problems. Regular blood tests are necessary to fine-tune the dosage.
Key Takeaways
- Levothyroxine is a synthetic T4 hormone that replaces what your thyroid doesn’t produce.
- It helps regulate metabolism, body temperature, heart rate, and more.
- Proper dosage is crucial and requires regular monitoring via blood tests.
- Take it on an empty stomach, at least 30-60 minutes before breakfast, with water.
- Avoid taking it with coffee, milk, calcium, or iron supplements as they can reduce absorption.
- Consistency in timing is key for stable body levels.
- Changes in dosage may be needed due to pregnancy, weight changes, or other medications.
- If a dose is missed, take it as soon as remembered, unless it’s close to the next dose.
- Avoid changing brands without consulting your doctor due to potential absorption differences.
- Store it in a cool, dry place, away from light, heat, and moisture.
- It can take 2-6 weeks for full symptom improvement.
- Hypothyroidism treatment is often lifelong.
- Regular blood tests (TSH and sometimes Free T4) are needed to confirm correct dosage.
- Certain foods (coffee, milk, soy) and supplements (iron, calcium) can interfere with absorption.
- Other medications (antibiotics, antacids, cholesterol drugs) may require timing adjustments.
- Taking it at night might be an option for some, but consistency is vital.
- Alcohol in moderation is generally okay, but excessive use can affect thyroid function.
- Side effects usually occur with incorrect dosage (e.g., anxiety, rapid heartbeat).
- Long-term high doses may be linked to bone issues and heart problems.
- Temporary hair loss can occur initially; persistent loss may indicate dosage issues or other causes.
- It’s safe and important during pregnancy and breastfeeding, often requiring dosage adjustments.
- It can improve fertility issues caused by hypothyroidism.
- It doesn’t interfere with most contraceptives, though some hormonal ones might slightly affect thyroid hormone transport.
- Caution is advised for individuals with heart conditions, severe osteoporosis, or a history of hyperthyroidism.
- It should NOT be used for weight loss if thyroid function is normal.
- It can help lower cholesterol if the high cholesterol is due to hypothyroidism.
- It can improve energy and mood in those with hypothyroidism.
- Normal dosage should not impair driving or cycling; however, if experiencing symptoms, exercise caution.
- Weight changes can necessitate dosage adjustments.
Levothyroxine vs. Other Hypothyroidism Treatments
Levothyroxine is the standard and most common treatment for hypothyroidism. It’s a synthetic hormone that precisely matches the T4 produced by the body. It’s easy to take, has a long half-life allowing for once-daily dosing, and is well-supported by scientific evidence. Older treatments, like dried thyroid extracts from animal sources (e.g., pork), contain both T4 and T3 but in variable and less predictable ratios. While some people might benefit from combinations of T4 and T3, levothyroxine is generally considered the most stable, safest, and scientifically backed option.
How to Take Levothyroxine Correctly
Taking levothyroxine properly is vital for its effectiveness. It should be taken once daily, on an empty stomach. The best time is usually in the morning, at least 30 to 60 minutes before breakfast, with a full glass of water. It’s important not to take it with food, coffee, milk, or supplements like calcium or iron, as these can significantly reduce its absorption, making the medication less effective. Maintaining a consistent daily schedule helps keep your body’s hormone levels stable.
What Is the Correct Levothyroxine Dosage?
There isn’t a one-size-fits-all dosage. Your dose will be tailored to you, considering your age, weight, overall health, and, most importantly, your blood test results. These tests measure thyroid hormone levels, including TSH (Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone), which is produced by the pituitary gland and directly relates to thyroid hormone levels. Dosage adjustments are typically made after several weeks of starting treatment, based on these results. It’s crucial not to alter your dosage on your own; always consult your doctor for adjustments.
Your dosage might also change if you become pregnant, experience significant weight fluctuations, or start taking other medications.
What If I Miss a Dose of Levothyroxine?
If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember, unless it’s almost time for your next dose. In that case, skip the missed dose and continue with your regular schedule. Do not take a double dose. Missing an occasional dose usually isn’t a major issue, but frequent missed doses can disrupt the treatment’s balance. If you find yourself often forgetting, consider setting phone reminders or asking a family member for help. Consulting your doctor or pharmacist can also provide strategies to help you remember.
Can I Change My Levothyroxine Brand?
Ideally, it’s best not to switch brands once you’ve found one that works well for you and your dosage is stable. Different brands contain the same active ingredient but may have variations in inactive ingredients (excipients) or absorption rates, which could potentially affect your blood levels. If a switch is necessary, discuss it with your doctor. If a pharmacy substitutes a different brand, inform your doctor so they can check if any follow-up tests are needed to ensure your hormone levels remain stable.
How to Store Levothyroxine Correctly
Proper storage is important to maintain the medication’s effectiveness. Store levothyroxine in a cool, dry place, protected from light, heat, and moisture. Avoid storing it in bathrooms or kitchens, as these areas can have fluctuating temperatures and humidity. The ideal temperature range is typically between 15-30°C (59-86°F). Do not freeze it or expose it to direct sunlight. Keep it in its original container until you’re ready to take it.
How Long Does Levothyroxine Take to Work?
You might start noticing effects within a few days, but significant improvements in symptoms typically take two to six weeks. This is because your body needs time to adjust its hormone levels. Some people feel better sooner than others, and the initial dosage can also influence how quickly you feel the benefits. Patience is key; stick with your treatment plan until your thyroid hormone levels are optimized and you feel better.
How Long Will I Need to Take Levothyroxine?
For most cases of hypothyroidism, treatment with levothyroxine is lifelong. However, there might be specific situations, such as temporary hypothyroidism during pregnancy or due to acute inflammation, where treatment might be time-limited. Any decision to stop or alter treatment must be made under strict medical supervision with appropriate monitoring.
How Do I Know If My Levothyroxine Dose Is Correct?
The most reliable way to know if your dose is correct is through blood tests. The primary test is for TSH, but your doctor may also order a test for Free T4. If your levels are within the normal range and you are not experiencing symptoms of either hypothyroidism (fatigue, slow metabolism) or hyperthyroidism (anxiety, rapid heartbeat, hair loss), your current dose is likely correct. If your levels are off or you have symptoms, your doctor will adjust your dosage. Never change your dose without consulting your doctor.
How Often Should Monitoring Tests Be Done?
When you first start treatment or after a dosage change, monitoring tests are usually done about six to eight weeks later. Once your dosage and hormone levels are stable, tests are typically repeated every six to 12 months. However, more frequent testing might be necessary if you experience new symptoms, become pregnant, have significant weight changes, or start new medications. Your doctor will determine the appropriate testing schedule for you. It’s important to get tested regularly, as symptoms don’t always perfectly reflect hormone levels.
What Foods or Drinks Can Interfere with Levothyroxine Absorption?

Several foods and drinks can hinder levothyroxine absorption if consumed close to the time of taking the medication. These include coffee, milk and dairy products, soy products, whole grains, fiber-rich foods, nuts, and cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and cabbage. Additionally, iron and calcium supplements, as well as antacids containing aluminum or magnesium, can interfere. To avoid this, take levothyroxine on an empty stomach and wait at least 30-60 minutes before eating or taking any other medications or supplements.
Can I Take Other Medications with Levothyroxine?
Yes, but with caution. Some medications can interfere with levothyroxine’s absorption or its effects. Besides the supplements and antacids already mentioned, this includes certain antibiotics, anti-seizure medications, cholesterol-lowering drugs, and some antidepressants. The key is to time them correctly. It’s often recommended to separate levothyroxine from these medications by at least four hours. Always inform your doctor or pharmacist about all medications and supplements you are taking to avoid interactions and ensure proper dosage and timing.
How Can Levothyroxine Absorption Be Improved?
As previously discussed, taking levothyroxine on an empty stomach, at least 30-60 minutes before breakfast with water, and avoiding interactions with food, coffee, or other medications is the primary way to improve absorption. Maintaining a consistent daily routine, taking it at the same time each day, is also crucial. Some individuals find that taking levothyroxine at night works better for them, provided they avoid eating for a few hours before and after. The most important factor is consistency and adhering to a regular schedule.
Can I Drink Alcohol If I Take Levothyroxine?

Moderate alcohol consumption generally doesn’t directly interfere with levothyroxine. However, regular or excessive alcohol intake can negatively impact liver function and thyroid function, potentially altering hormone levels and how the medication is metabolized. If you have pre-existing liver or heart conditions, alcohol can worsen these issues. It’s best to limit alcohol intake while taking levothyroxine. If you have any doubts or concerns, discuss them with your doctor, especially if you have other health conditions or take multiple medications.
What Are the Most Common Side Effects of Levothyroxine?
When taken at the correct dosage, levothyroxine is usually well-tolerated and doesn’t cause significant problems. However, if the dose is too high, side effects can occur. These may include nervousness, rapid heartbeat, insomnia, increased sweating, tremors, weight loss, headaches, and digestive issues like diarrhea. These symptoms are typically a sign of too much thyroid hormone in the body and indicate that your dosage needs adjustment by your doctor.
Long-Term Effects of Levothyroxine
When taken at the appropriate dose, levothyroxine generally does not cause adverse long-term effects. However, taking excessively high doses for extended periods (months or years) has been linked to an increased risk of bone thinning (osteoporosis) and heart problems, particularly in older adults. Regular monitoring and dosage adjustments are essential to prevent these potential long-term issues. If your dosage is correct, levothyroxine is a safe medication.
Can Levothyroxine Cause Hair Loss?

Some temporary hair thinning can occur in the first few months of starting levothyroxine as your body adjusts to the treatment. This usually resolves on its own. However, persistent or severe hair loss might not be due to the medication itself but could be a symptom of the underlying hypothyroidism or other factors like stress, nutritional deficiencies, or other health issues. If you experience significant hair loss, consult your doctor to determine the cause and whether your dosage needs adjustment or if other factors are at play.
Is Levothyroxine Safe During Pregnancy or Breastfeeding?
Yes, levothyroxine is safe and crucial for pregnant individuals with hypothyroidism. Untreated hypothyroidism can harm the baby’s development and increase the risk of complications. During pregnancy, your levothyroxine dosage may need to be increased due to hormonal changes. It’s also safe to take while breastfeeding, as only small, safe amounts pass into breast milk. However, regular medical monitoring and blood tests are essential in both pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Can Levothyroxine Cause Fertility Problems?
No, it’s the opposite. Untreated hypothyroidism can lead to fertility issues in both men and women. Properly treating hypothyroidism with levothyroxine helps normalize thyroid hormone levels, which can significantly improve fertility.
Does Levothyroxine Affect Contraceptives?
Levothyroxine generally does not interfere with contraceptives, whether hormonal or barrier methods. However, some combined hormonal contraceptives might affect the transport proteins for thyroid hormones, potentially reducing the effectiveness of levothyroxine. These interactions are usually minor, but if you notice any changes in your symptoms, consult your doctor for monitoring and possible dosage adjustments.
Are There Any Contraindications or Special Precautions for Levothyroxine?
While there are few absolute contraindications, it’s important to inform your doctor about any existing medical conditions or other medications you are taking. Special caution is advised for individuals with heart conditions (like arrhythmias or recent heart attack), severe osteoporosis, or a history of hyperthyroidism. Elderly individuals and those with intestinal absorption issues may also require closer monitoring and dosage adjustments. Your doctor will assess your specific situation to ensure safe and effective treatment.
Can Levothyroxine Be Used for Weight Loss?

No, levothyroxine should not be used for weight loss if your thyroid function is normal. Using it without a medical need can lead to serious side effects like anxiety, insomnia, muscle loss, and heart problems. It is only intended for treating hypothyroidism. In cases where hypothyroidism has caused weight gain, levothyroxine can help restore a healthy weight, but it is not a weight-loss drug.
Does Levothyroxine Affect Cholesterol Levels?
Hypothyroidism can lead to elevated cholesterol levels, particularly LDL (‘bad’) cholesterol. By treating hypothyroidism with levothyroxine, thyroid function is normalized, which in turn helps to lower cholesterol levels naturally. Levothyroxine isn’t a cholesterol medication itself, but it addresses an underlying cause of high cholesterol. Doctors often check for hypothyroidism in patients with high cholesterol and treat it first.
Can Levothyroxine Affect Energy Levels and Mood?
Yes, when taken at the correct dose, levothyroxine can improve energy levels, mood, concentration, and motivation in individuals with hypothyroidism, as the condition itself can cause fatigue, apathy, and depressive symptoms. Conversely, taking too much levothyroxine can lead to nervousness, anxiety, insomnia, and feeling overly stimulated. The key is finding the right dosage to achieve optimal physical and mental well-being.
Can I Drive or Cycle While Taking Levothyroxine?
You can generally perform normal activities like driving or cycling as long as your dosage is correct, symptoms are managed, and hormone levels are stable. Levothyroxine does not typically cause drowsiness or impair reaction times. However, if you are just starting treatment or your dosage is not yet optimized, and you experience symptoms like dizziness, excessive fatigue, or poor concentration, it’s best to exercise caution and wait until your hormone levels stabilize before engaging in these activities.
How Do Weight Changes Affect the Required Levothyroxine Dose?
Your weight is a factor in determining your levothyroxine dosage, especially when starting treatment. Significant weight gain or loss, such as during pregnancy or after major dietary changes or surgery, can alter your body’s hormonal needs. In such cases, monitoring tests are necessary to check your hormone levels and determine if your levothyroxine dosage needs adjustment. Changes in muscle mass or intestinal absorption can also influence dosage requirements. Your doctor will evaluate these factors based on lab results and your symptoms to make any necessary adjustments.
Source: Dr. Alberto Sanagustín